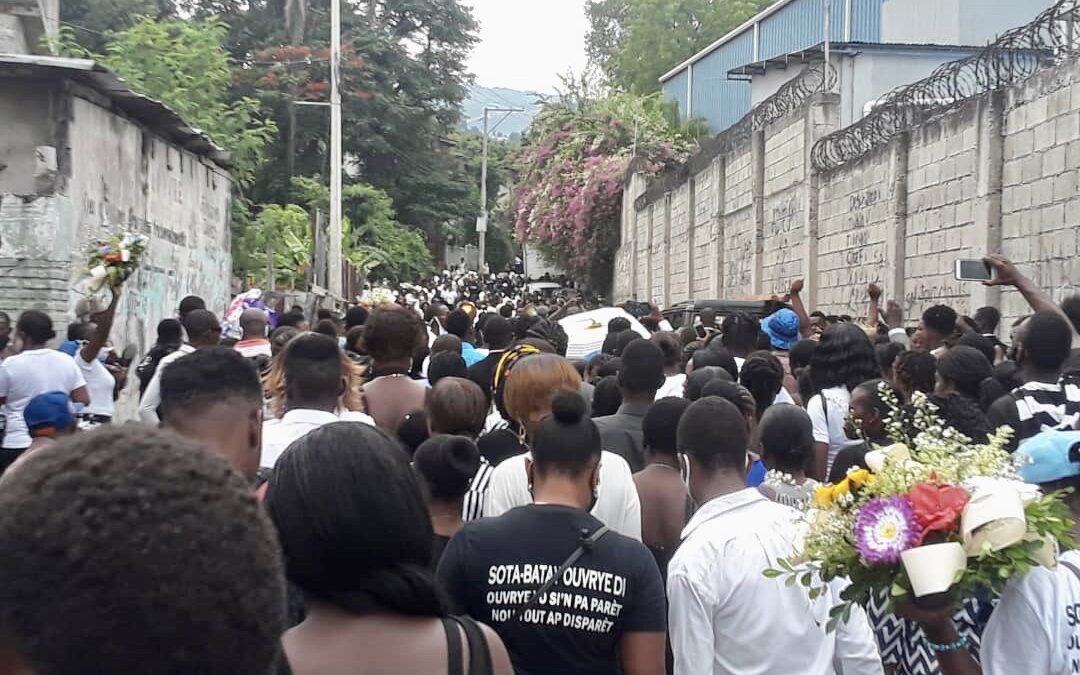Garment workers in Haiti are calling for action after Sandra René, a garment worker at the Palm Apparel factory, died due to pregnancy complications in early August. René was turned away from the hospital where she sought medical care because the factory had not paid into the health insurance system for occupational injury, sickness and maternity (OFATMA) on her behalf, as legally required.
Hundreds of garment workers marched with René’s casket in a funeral procession to the OFATMA offices to protest her death. A 10-year employee with the factory, René was six months pregnant when she sought medical care and died at her home four days later. The country’s garment industry is the second largest source of formal employment for workers in Haiti, where the majority of 57,000 garment workers are women and often the only wage earners for their families.
With their unions, the Association of Textile Workers Unions for Re-importation (GOSTTRA) and Workers Struggle (Batay Ouvriye), workers are demanding that employers meet their legal obligations so Haitian workers can access health care, especially critical during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Few Garment Factories Pay into Required Health, Pension Funds
Few factories make the required contributions to the health or pension funds. Some 83 percent of factories were noncompliant with such legal requirements between April 2019 and March 2020, according to Better Work Haiti (BWH). Employers are required to register workers in the system, and both employers and workers must contribute the equivalent of 3 percent of the employees’ wages for the past pay period to OFATMA. The employer is responsible for deducting the employees’ contributions from paychecks but often either do not register workers or take paycheck deductions without sending the funds to OFATMA.
Garment workers began returning to the job as early as April when factories reopened after shuttering for a month to prevent spread of the novel coronavirus. Desperate for wages to support themselves and their families, workers risk COVID-19 exposure during crowded work commutes.Workers say they fear they will not have access to health care if they become ill because employers are not paying into OFATMA.
Income inequality is widening in Haiti, which remains among the most unequal countries in the world. The persistence of high levels of inequality is due in part to a concentration of resources in the hands of a small but powerful group of elites, and the weakness or absence of channels of resource redistribution, such as targeted transfers and a social safety net, according to the International Monetary Fund.
Further, the minimum wage for garment workers in Port-au-Prince, the capital, is at least four times lower than the cost of living, according to a 2019 Solidarity Center survey. Since the pandemic, workers no longer work a standard 48-hour workweek, reducing their pay and making them ineligible to receive one day of paid rest per week.