Mar 8, 2021
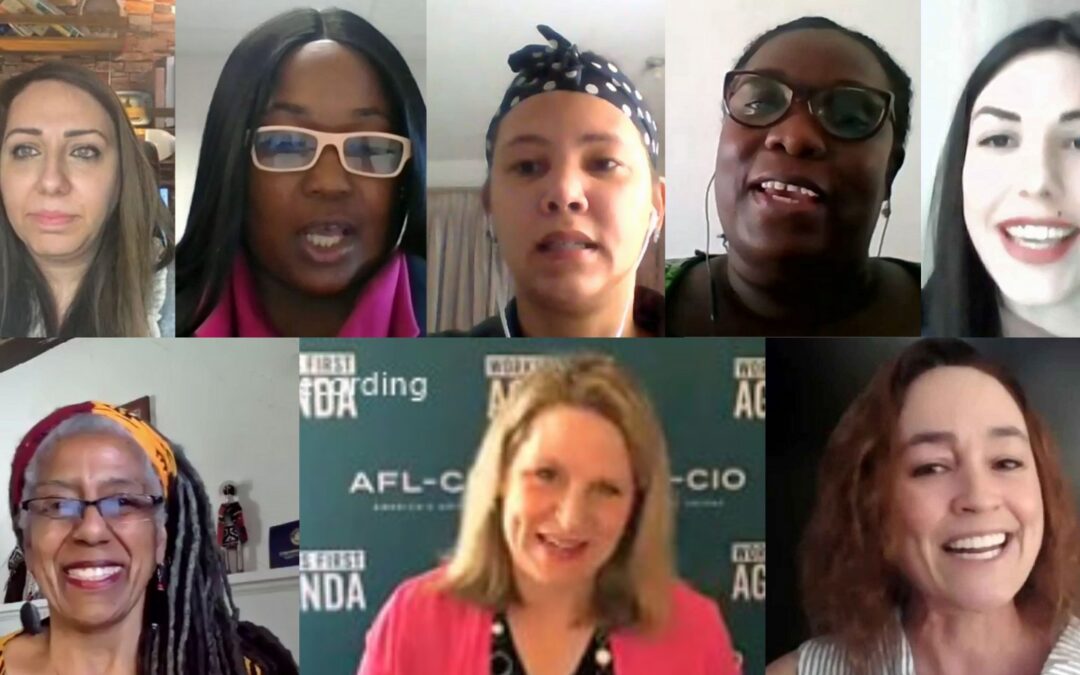
Women are undervalued, underpaid and the target of disparaging stereotypes and even violence—but by joining together in unions, they stand strong with a collective voice to change the workplace, society and government, women union leaders said today in a panel event.
“Women are carrying the burden. But we are not remaining silent,” said AFL-CIO Secretary Treasurer Liz Shuler, in opening remarks. “We are claiming our power through our union. It’s one of the most important stories in the world. It is about our collective power.”
Marking International Women’s Day, March 8, the panel, “Ever Essential: Women’s Work Is the Backbone of the Global Economy,” featured leaders from Colombia, Ghana, Palestine and the United States who shared their experiences defending the rights of women workers to equality, good jobs and an end to violence and abuse. Nearly 200 participants joined the virtual panel, sponsored by the Solidarity Center and the U.S.-based Coalition of Labor Union Women (CLUW).
CLUW President Elise Bryant launched the event with a song and a salute to “SNAP”: Sisters Not Afraid of Power. “The rest of the world has finally figured out what we always knew: Women’s work is essential. Period,” she said.
Gaining a Place in Union Leadership, Government
“Women’s work is underpaid even though the work they do makes society function,” said Philadelphia CLUW President Koren M. Parker, adding that globally, women work 4.5 unpaid hours a day compared with slightly more than two hours a day for men.

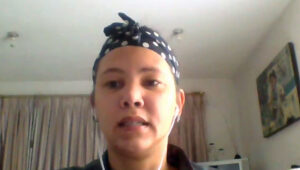
Emelia Ghansah recounted her rise in union leadership despite the obstacles she faces as a woman. Credit: Solidarity Center
Women’s struggles to gain their rightful place in leadership and decision-making positions also includes unions, said Emelia Ghansah, the training and education leader at the General Agricultural Workers’ Union of Ghana (GAWU).
“Even though we are the majority, our voice does not reach the top,” she said. While women work to elect men to leadership positions, support for women who seek high office “is never reciprocated by men.”
Ghansah, who described how she rose from a program officer to her current position despite obstacles to women’s union participation like lack of child care, recently worked with street vendors, primarily women, helping organizing them to work collectively and accompanying them as they met with local authorities to negotiate for a new market building, now underway.
In Palestine, Sanaa Alsarghali from the nongovernmental organization Women, Media and Development, shared how she is talking with university students, working women and other groups to gain support for ensuring women are included in process to draft a new constitution, one that addresses gender-based violence and ensure gender equality.
‘Only Our Collective Power Could Win’
In Colombia, Carolina Del Valle Hevia de Brandts led the formation of a union representing more than 1,000 Colombian and Venezuelan workers delivering food from restaurants and grocery stores to homes.
Carolina Del Valle Hevia de Brandts founded a union for food delivery drivers in Colombia. Credit: Solidarity Center
While digital platforms like food delivery and ride sharing “have amassed a lot of money during the pandemic all over the world,” workers, especially women, have few rights and are vulnerable to abuse, said Hevia. “Women face sexual harassment, violent threats and all kinds of behavior just because we are working the public space and streets [that] are our working environment,” she said.
A refugee from Venezuela, Hevia described how women migrant workers are doubly targeted because of ethnic stereotypes. Yet by joining together in the Union of Platform Workers (UNIDAPP), Hevia said she and other union members are “defenders of people’s rights so we can become a better society with no distinction of race or gender.”
“When we unite, we are invincible!”
In a rousing close, Solidarity Center Executive Director Shawna Bader-Blau said the panel provided women with inspiration and energy to go forward.
“When we get tired, we can still be inspired. Let’s carry the truth that we are stronger together.
When women workers’ win, everybody wins. When women workers stand up, women change the world!”

Feb 24, 2021
Teachers in Jordan are “insisting on their legal rights to have an association” and will not give up after the government dissolved their union in July and imprisoned union activists, says Kefah Abu Farhan, a board member with the Jordan Teacher Association (JTA).
بالعربية
“Teachers, male and female, stress day after day that these measures are not acceptable for us and we will not back down until the teachers association goes back to its legal standing,” said Abu Farhan, speaking recently with the Solidarity Center through a translator.
The JTA, representing 140,000 active members, waged a month-long strike in 2019 when the government failed to respond to its demand for a 50 percent salary increase. As a result of the strike, teachers received a 35 percent wage increase and 14 additional improvements, the most important of which was the union’s participation in managing the teachers’ savings fund, with its assets totaling more than $141 million.
In July 2020, police raided JTA headquarters in Amman, the capital, and 11 of its branches across Jordan and jailed thousands of teachers, including JTA chairman Nasser Nawasreh. The teachers, some of whom went on a hunger strike, were released after spending a month in prison. Many are still being prosecuted in court, says Abu Farhan. In addition, the government forced 62 teachers to take early retirement “as punishment for expressing their views,” said Hala Ahed, a lawyer on the JTA’s legal team, speaking with the Solidarity Center. The government dissolved the JTA for two years in December 2020 and imprisoned its board members for one year.
Crackdown on Union Freedom Dangerous Road for Democracy
The Jordan government’s move to shut down the JTA was denounced by the global labor movement and human rights organizations worldwide. The United Nations Human Rights Commission said the action is “emblematic of a growing pattern of suppression of public freedoms and the restriction of civic and democratic space by the Jordanian government, including against labor rights activists, human rights defenders, journalists and those who have peacefully criticized the government.”
In October, Jordan authorities barred the JTA from holding a press conference to discuss the conditions teachers are experiencing, a ban implemented by security forces delivering an order from the Amman governor.
Jordanian civil society organizations and unions drafted a solidarity letter condemning measures targeting the right to form unions and other civic freedoms. The JTA’s success in winning the government’s agreement to sign a collective bargaining contract, and the strong stance of teachers demanding their rights, attracted broad public support. The government shut down the JTA in part because it “has become ground zero for those who want to gather, for the middle class to voice their dissatisfaction,” says Ahed.
“There is a symbolic message sent here: Officials can encroach upon constitutional freedoms and escape punishment,” she said. “This could be indication that the upcoming period will be one of oppression, suppression, restraining freedoms in very blunt manner. This is very dangerous.”
Reversing the Gains of the 2011 Arab Uprising
The teachers’ union was established in 2012 after the Jordan monarchy issued a royal decree, reviving the union suspended in the 1950s. Expanded freedom to form unions was among some of the civic freedoms working people championed and won during the 2011 Middle East and North Africa Arab uprisings. In 2011, Jordan amended its constitution, giving political parties and unions the right to form.
Teachers had fought for their rights to form unions and collectively bargain for decades, with many imprisoned in 1975 for setting up committees to create a union. After a new teacher’s movement arose in the 1990s, they were barred again from unionizing when the government cited the constitution to justify its refusal to recognize a teacher’s union.
The victories of 2012 “occurred because of the sacrifices of workers,” says Abu Farhan. “It’s very dangerous, very dangerous, for unions to lose their rights.” Although the country’s constitutional court has recognized International Labor Organization Convention 87 on the right to freedom of association, the government has not yet ratified it.
The government shuttered the JTA after it asked members on Facebook to weigh in on how to ensure the government follow up with its promised pay increases. One of the suggestions called for sit-ins and demonstrations, and proposed activities also included thinking about participating in or boycotting national elections.
The JTA did not commit such a violation of the law because it did not call for an election boycott and calling for demonstrations is not illegal, says Ahed. “There was no criminal act,” she said. “The criminal act under this count only applies to physically preventing people from coming to vote.” During the court trial of JTA Board members, no witnesses were allowed for the defense, she said.
“When the JTA is no more, we go back to pre-2012 days,” Abu Farhan said. “Teachers have to claim their rights, lobby, advocate for their rights. On top of that, we have deteriorating conditions of teachers and their difficulty in retaining top-notch performance. We go backward regarding future reforms in Jordan.”
Yet as Abu Farhan said, teachers will not be silenced: They protested in January even as Jordanian security forces barricaded the roads leading to the Jordan legislature in Amman. The government also placed a metal fence around an open area opposite the parliament in an attempt to prevent large gatherings.
Throughout their protests, teachers carry signs supporting the freedom to negotiate for better wages and working conditions through their freely formed union: “My union is a national achievement that Jordanian teachers will not give up on,” and, simply, “Bring back the teachers’ union.”
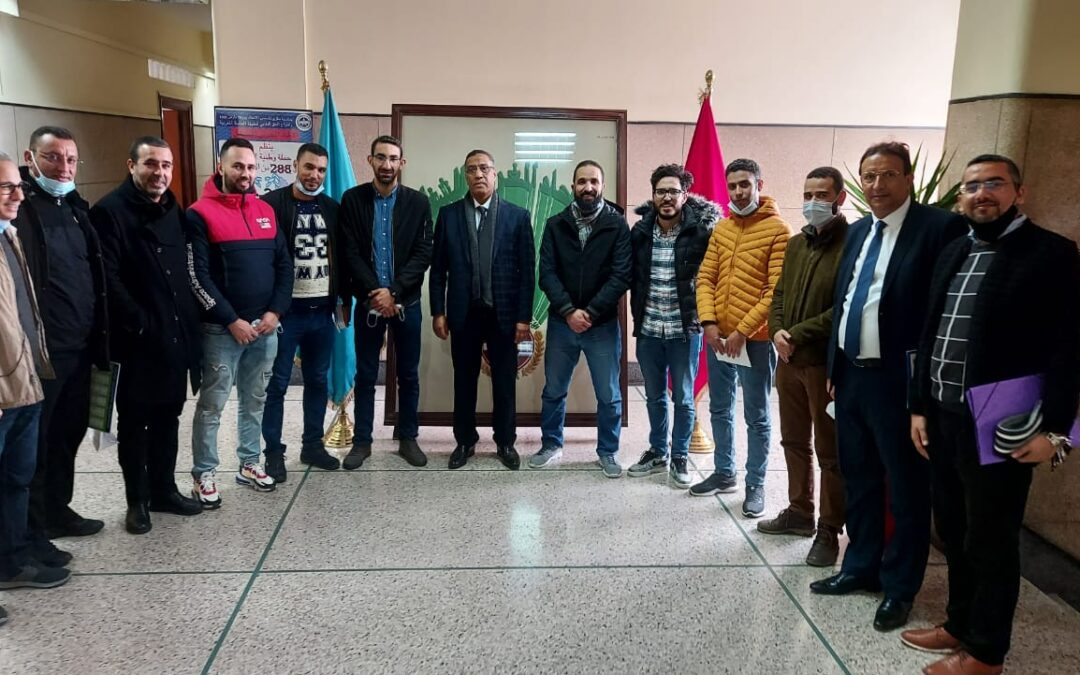

Feb 23, 2021
Workers in Morocco are denouncing efforts by a Peugeot Citroen factory to force union leaders to resign from the Moroccan Labor Union (UMT) or lose their jobs. Already, one union leader has been fired, according to the union.

One worker was injured during a closed-door session with factory employers, according to UMT. Credit: UMT
Last week, factory management forced 11 union activists to sign resignation letters after compelling them to spend three hours behind closed doors where union leaders say they were subjected to questioning and harassment that seriously injured one worker.
“This violation of workers’ rights sullies the image of our country,” UMT says in a statement. “We call upon all local authorities to intervene in our case, and we call for the solidarity of workers at the company, and from unions across Morocco.”
Union members met in a general assembly over the weekend, where they stood strong for their rights to form a union and bargain collectively, and proceeded with planned union elections.
Over the past few months, the workers have protested the non-payment of overtime at the factory and waged a strike earlier this year at the plant in Kenitra, on Morocco’s northwestern coast. In 2019, Peugeot SA recorded more than $4 billion in profits.
The General Confederation of Labor (CGT) in France, which represents workers at Peugeot, supported the workers’ strike in Kenitra and vowed to assist them in their current struggle.
Union leaders say they expect management to announce this week whether the workers forced to sign resignation letters will be officially fired.

Feb 11, 2021
A 14-year old girl was among the 28 garment workers killed in a factory disaster in Tangier, Morocco, this week. Her mother says she had worked at the factory, an illegal sweatshop, for three years.
The workers were drowned or electrocuted after a flood caused a short circuit. Seventeen others were injured. The facility operated in an underground garage in a residential area with 130 workers, most of them women. A nearby resident rescued some of the workers by throwing a rope into the flooded factory.
“How could this factory have been a secret? Where were the labor inspectors? Where were the local government authorities? Where were the investors?” asked Amal El Amri, a representative in Morocco’s upper house of Parliament and Moroccan Labor Union (UMT) member.
Residents in the area say the sweatshop operated for more than 20 years.
“We must ensure a voice for these workers who have died, and for the many thousands more women workers who toil under the same dangerous conditions,” El Amri said. In January, a fire at another illegal textile factory in Tangier injured one person and destroyed the factory, where 400 people worked.
The UMT and Democratic Labor Confederation (CDT), both Solidarity Center partners, demanded an immediate investigation into the tragedy, and the CDT said in a statement that it holds the state, the government and the employers fully responsible for the workers’ deaths.
Fast Fashion Industry Spawns Illegal Factories
Across from Spain on Morocco’s northern coast, Tangier is a key hub of Morocco’s textile manufacturing. Countrywide, official statistics show 1,200 textile companies with 165,000 workers—27 percent of the country’s industrial employment.
Yet many factories in Morocco’s textile and leather industry—estimates range in the thousands—operate illegally, forcing workers to labor long hours for low pay in often dangerous conditions. A 2012 investigation revealed that workers in illegal Moroccan textile sweatshops work, on average, 55 to 65 hours per week—11 to 21 hours more than the legal limit.
Operating outside national labor laws or standards, illegal factories are a direct response to the demands of the fast fashion industry, in which large brands demand quick response to fashion changes and customer demands and so draw on subcontractors whose workforce is cheaper and its work arrangements informal.
With no job stability and few social protections, garment workers in the informal economy are subject to exploitation and abuse, with no health coverage, pensions or other social and legal protections. Some one-third of Morocco workers are in the informal economy, which accounts for 14 percent of the country’s gross domestic product.
‘Companies Must Be Held Accountable’
As the global labor movement joins in calls for accountability in a supply chain where workers pay the price for cheap production, the Morocco Contribution Forum is urging the government to close all workplaces without health and safety protections and establish a policy to ensure severe penalties for companies operating outside the law.
Public officials must “improve the rights and living standard of marginalized people who are victims of oppression and violence, whether it is on the way to work, or in the workplace, and to provide them with the minimum conditions of human rights,” the Forum, a Solidarity Center partner, said in a statement.
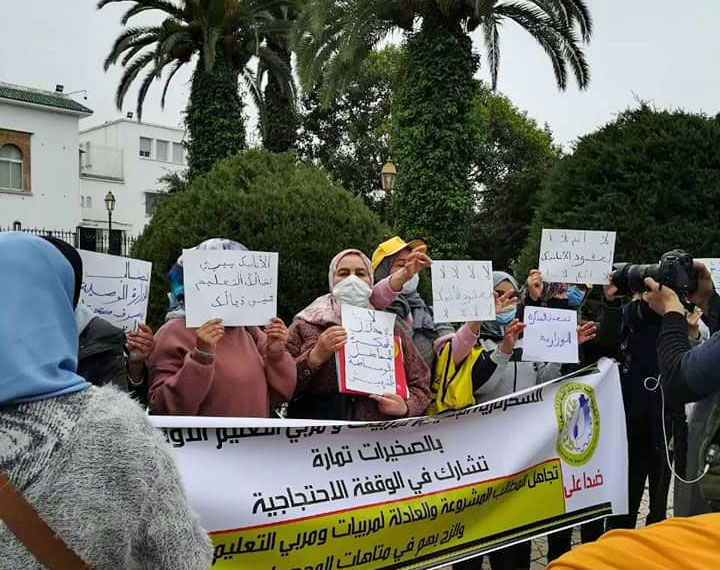

Feb 4, 2021
Teachers carried out protests throughout January against a government crackdown on their fundamental freedom to strike, with rallies at the Ministry of National Education and Vocational Training in the capital, Rabat, and across the country. Teachers also are protesting the working conditions of contractual teachers and the Ministry of Education’s refusal to engage in social dialogue.

The CDT is calling for nationwide protests February 10 around education worker demands. Credit: CDT
Morocco’s constitution has protected the right to strike since 1962, but the government seeks to revise the country’s labor law by adding significant obstacles to the right to strike, in violation of Morocco’s international legal obligations. Unions are calling on the government to engage in real social dialogue to develop legislation consistent with international law.
“These abusive measures constitute a flagrant violation of the constitution, of the guarantee of the right to strike and of national laws, as well as against international conventions that consider the right to strike a fundamental part of freedom of association,” the Democratic Labor Confederation (CDT) wrote in a December letter to Educational International. The global federation, Education International, strongly supports the CDT and the National Union of Teachers (SNE) in their efforts to push back against the government’s moves to limit essential worker rights.
The government also barred a planned December 22 sit-in on at the Education Ministry headquarters in Rabat, citing exceptional circumstances and the law on health emergencies. Union members and leaders called the ban illegal and said security service used force to disperse them before they could reach the Ministry’s headquarters.
The January actions follow a series of rallies and sit-ins across Morocco last fall, including a national general strike on December 1 and 2, as teachers protested the government’s move to reduce their seniority and promotion opportunities and its replacement of full-time teachers with teachers on contract who are paid lower wages and have no job security.
Education Officials Refuse to Meet with Teachers
Morocco’s workers and their unions have been left out of discussions regarding management of the COVID-19 crisis and educational continuity, according to the SNE-CDT. The union says the ministry has not fully addressed health and safety conditions for teachers, education support staff and pupils.
Education ministry officials have frozen dialogue with teachers, last meeting with them in February 2019. One of the union’s fundamental demands is for the government “to open a serious and responsible dialogue on the outstanding demands from 2014 to today, and the respect of trade union freedoms and the right to strike.” Among the unresolved issues are improved wages, a voice for teachers in the education reform process, investment in public education, teacher training and more staffing to lower classroom size.
In early January, the CDT also spoke out against the ministry’s unilateral decision to cancel upcoming examinations for middle and high school students due to the pandemic, highlighting another example of how the education ministry fails to involve the representatives of teachers and other employees of the public school system in decision making.
More Teachers on Contract, with Few Rights
In early 2019, a government decree removed the option of workers with renewable two-year employment contracts to integrate into the public sector, a move that means contract teachers have no access to fair wages and social benefits like pensions, health care or job security. The CDT has sought to replace fixed-term contracts with permanent employment.
The number of fixed-term teaching contracts is increasing in Morocco and undermines the core notion of public service. The change grants the government a waiver on its obligations, according to a recent CDT field study on the future of work in the education sector, carried out in collaboration with the Solidarity Center. “Some of the direct results of casualization, as identified through the study, include instability, precariousness, dissatisfaction and lack of confidence in the profession’s future,” the CDT notes.
The study also finds an increasing number of women in all levels of the education system, and the future of work in the education sector must address this shift, says Younes Firachin, a member of the National Office of the National Education Union. That requires unions “to fully grasp these transformations” to effectively reach them and address their concerns, he says.
Employees throughout the public education system, frustrated by the lack of attention to their terms and conditions of employment, increasingly are joining the protests. On January 27, many who provide assistance to young children in kindergarten and primary school rallied in Rabat.
The CDT also announced a series of nationwide protests set for February 10 to mobilize administrative and technical assistants to call for their recognition by the Ministry of Education and Morocco’s public school system.









